All Categories
Featured
2 individuals purchase joint annuities, which supply a surefire earnings stream for the rest of their lives. When an annuitant passes away, the interest earned on the annuity is dealt with in a different way depending on the type of annuity. A kind of annuity that stops all payments upon the annuitant's fatality is a life-only annuity.
The original principal(the quantity initially deposited by the moms and dads )has actually already been strained, so it's not subject to taxes again upon inheritance. The revenues section of the annuity the interest or investment gains accrued over time is subject to income tax. Commonly, non-qualified annuities do.
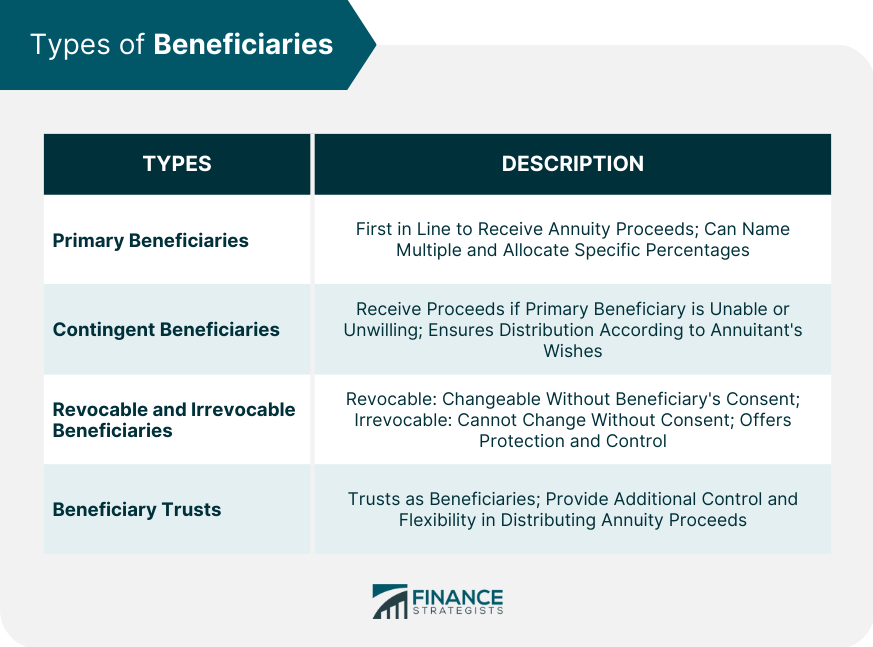
have actually passed away, the annuity's benefits usually return to the annuity owner's estate. An annuity proprietor is not lawfully required to inform existing recipients regarding changes to beneficiary designations. The choice to alter recipients is generally at the annuity proprietor's discretion and can be made without alerting the current recipients. Because an estate technically doesn't exist till a person has passed away, this recipient classification would only enter impact upon the fatality of the named individual. Normally, as soon as an annuity's owner passes away, the marked recipient at the time of fatality is qualified to the advantages. The spouse can not alter the beneficiary after the owner's death, even if the beneficiary is a minor. There might be details provisions for handling the funds for a small recipient. This often involves designating a guardian or trustee to take care of the funds up until the youngster gets to adulthood. Generally, no, as the beneficiaries are not responsible for your financial debts. Nonetheless, it is best to speak with a tax obligation expert for a details response relevant to your situation. You will proceed to get settlements according to the agreement routine, however attempting to obtain a round figure or lending is likely not a choice. Yes, in almost all instances, annuities can be acquired. The exception is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payout option via annuitization. This sort of payout stops upon the death of the annuitant and does not supply any recurring worth to beneficiaries. Yes, life insurance policy annuities are usually taxed
When withdrawn, the annuity's profits are taxed as ordinary income. The primary quantity (the preliminary financial investment)is not exhausted. If a beneficiary is not called for annuity advantages, the annuity continues normally go to the annuitant's estate. The circulation will certainly comply with the probate process, which can postpone repayments and might have tax obligation implications. Yes, you can name a count on as the beneficiary of an annuity.
Are Structured Annuities taxable when inherited

Whatever part of the annuity's principal was not already exhausted and any profits the annuity collected are taxed as income for the beneficiary. If you inherit a non-qualified annuity, you will just owe taxes on the incomes of the annuity, not the principal used to purchase it. Because you're receiving the entire annuity at once, you have to pay tax obligations on the whole annuity in that tax year.
Latest Posts
Analyzing Strategic Retirement Planning A Closer Look at Fixed Indexed Annuity Vs Market-variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosi
Understanding Tax Benefits Of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities Everything You Need to Know About Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity What Is What Is A Variable Annuity Vs A Fixed Annuity? Pros and Cons of
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works Breaking Down the Basics of Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities Features of Smart Investment
More
Latest Posts